What is Artificial Intelligence? – Its Benefits and Future
Artificial Intelligence (AI) develops computer systems to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. This revolutionary field creates intelligent machines that perceive their environment, reason logically, and acquire knowledge from data. Furthermore, these machines effectively make decisions to accomplish specific objectives.
AI includes diverse subdomains such as robotics, computer vision, natural language processing, and machine learning. By automating processes, enhancing efficiency, and unlocking new possibilities, AI has the potential to transform various industries profoundly. The wide-ranging applications of AI include virtual assistants, self-driving cars, medical diagnosis, and financial forecasting.
As AI continues to advance, it inevitably gives rise to significant ethical and societal concerns. Consequently, it becomes an enthralling and thought-provoking field that merits exploration.

How does Artificial Intelligence (AI) Work?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) utilizes algorithms and data to simulate human intelligence in machines. The process can be summarized as follows.
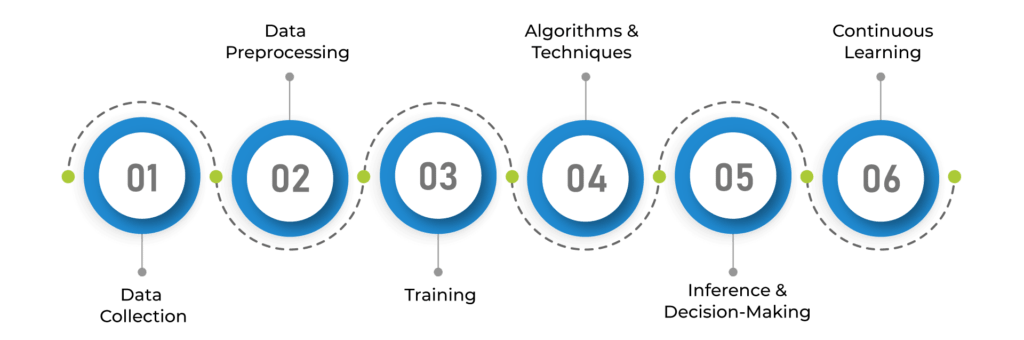
1. Data Collection:
AI systems require vast amounts of data, including structured and unstructured formats such as text, images, audio, and video. Data is collected from diverse sources like databases, sensors, and the internet.
2. Data Preprocessing:
Collected data undergoes preprocessing to clean and transform it into a suitable format for analysis. This involves tasks like reduplication, handling missing values, and data normalization.
3. Training:
Machine Learning algorithms train AI models by utilizing them to learn patterns and relationships in the data by adjusting internal parameters based on feedback. They divide the data into training and validation sets and then iteratively optimize the model to minimize errors or maximize performance.
4. Algorithms and Techniques:
AI employs various algorithms and techniques based on the task. Labeled data is used in supervised learning. Unlabeled data is analyzed to find patterns in unsupervised learning, and trial and error with reward-based feedback is used in reinforcement learning to learn.
5. Inference and Decision-Making:
Trained models make inferences and decisions by applying their knowledge to new, unseen data. They process input data to generate desired outputs or predictions.
6. Continuous Learning:
AI systems improve over time through continuous learning. Additionally, they adapt to new data and refine models. Furthermore, they update decision-making capabilities to remain relevant and accurate. Moreover, AI relies on computational power, often utilizing specialized hardware like GPUs to efficiently process complex calculations and large-scale data.
What are the Types of Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be classified into three main types:
1. Narrow or Weak AI:
Narrow AI, also known as weak AI, pertains to AI systems tailored for particular tasks or issues within a confined domain. For instance, voice assistants, recommendation systems, and image recognition software are notable examples. However, it is essential to note that narrow AI exhibits a focused and specialized nature devoid of general intelligence.
2. General or Strong AI:
General AI aims to possess human-level intelligence and perform intellectual tasks that humans can do across various domains. The goal is to create systems that understand, learn, and apply knowledge in different contexts. Achieving general AI remains a challenging ongoing endeavor.
3. Artificial Superintelligence:
Furthermore, in virtually all aspects, artificial superintelligence surpasses human intelligence. Additionally, these hypothetical systems demonstrate advanced cognitive abilities, enabling them to excel in complex problem-solving, decision-making, and creativity. Nevertheless, it is essential to note that artificial superintelligence is currently a theoretical concept and remains so at present.
Today, people widely use Narrow AI while researchers and experts are still researching and debating the development of General AI and artificial superintelligence.
What are the Advantages of Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) provides several advantages:
1. Automation : AI automates repetitive tasks, improving efficiency and freeing up human resources for more complex work.
2. Decision-Making : AI analyzes data and makes data-driven decisions faster and more accurately than humans, leading to better decision-making and outcomes.
3. Personalization : AI enables personalized experiences through recommendation systems and tailored content, enhancing customer satisfaction.
4. Efficiency : AI streamlines processes, optimizing workflows and reducing errors, thereby increasing operational efficiency and productivity.
5. Insights : AI uncovers valuable insights from large datasets, enabling data-driven analysis, trend identification, and predictive modeling for strategic planning.
6. Customer Service : AI-powered chatbots provide prompt and consistent customer support, improving satisfaction and reducing response times.
7. Medical Advancements : AI aids in medical imaging, disease diagnosis, and drug discovery, leading to faster diagnoses, treatment planning, and improved patient outcomes.
8. Safety and Security : AI enhances cybersecurity through threat detection, anomaly detection, and fraud prevention, bolstering protection against cyber threats.
While AI offers significant benefits, ethical and societal considerations are crucial for responsible development and deployment, addressing potential risks, and ensuring fairness in its application.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Different Industries
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has a wide range of applications across various industries:
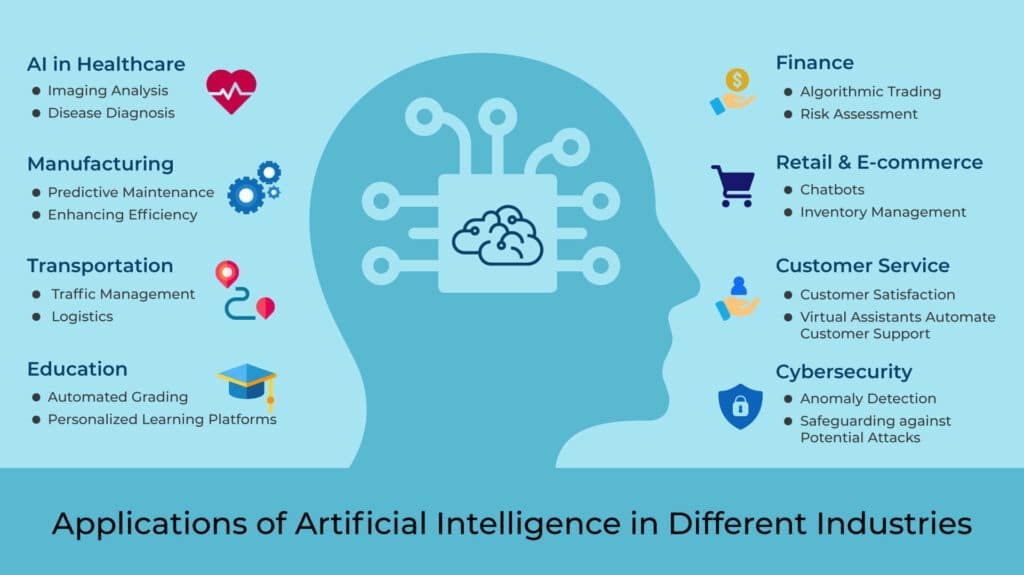
1. AI in Healthcare : AI aids in medical imaging analysis, disease diagnosis, and personalized medicine, improving patient care and treatment outcomes.
2. AI in Finance : AI is used for fraud detection, algorithmic trading, credit scoring, and risk assessment, enhancing efficiency and decision-making in financial institutions.
3. AI in Manufacturing : AI optimizes production processes, predicts maintenance needs, and enables robotic automation, increasing productivity and quality control.
4. AI in Retail and E-commerce : AI powers recommendation systems, chatbots, and inventory management, providing personalized shopping experiences and efficient customer support.
5. AI in Transportation : AI enables self-driving vehicles, traffic management systems, and predictive maintenance, improving safety, efficiency, and logistics.
6. AI in Customer Service : AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants automate customer support, enhancing response times and customer satisfaction.
7. AI in Education : Intelligent tutoring systems, personalized learning platforms, and automated grading utilize AI to enhance individualized instruction and student engagement.
8. AI in Cybersecurity : AI assists in threat detection, anomaly detection, and behavioral analysis, strengthening cybersecurity measures and safeguarding against potential attacks.
These are just a few examples, as AI is also used in agriculture, energy, gaming, and many other industries. AI’s ability to automate tasks, analyze vast amounts of data, and make intelligent decisions drives innovation and transforms businesses’ operations. However, ethical considerations and responsible implementation of AI are crucial to ensure its positive impact and address potential risks.
Future of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) promises a bright future and stands ready to revolutionize various aspects of our lives. Furthermore, advancements in automation will boost efficiency and productivity across industries, ultimately freeing humans from more complex tasks. Moreover, personalization will be significantly boosted, as experiences will be tailored based on individual preferences and behaviors, thus improving customer satisfaction.
1. AI will assist in disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized treatment plans in healthcare, resulting in faster and more accurate diagnoses and improved patient outcomes.
2. Furthermore, alongside the growing significance of ethical considerations and responsible AI usage, there will be an increasing focus on regulations targeting biases and guaranteeing transparency in AI development and deployment. Additionally, an upsurge in human-AI collaboration is expected as organizations and industries harness AI technology to enhance human abilities and effectively address complex challenges.
3. Ongoing research and innovation will focus on developing more powerful algorithms and improving machine learning techniques, leading to computer vision, robotics, and cognitive computing breakthroughs.
4. The socioeconomic impact will require reskilling and adaptation to new roles, necessitating collaboration between governments, industries, and educational institutions.
Conclusion
AI evolves daily and solves more problems accurately. It has good potential to improve the productivity of humans. It automates many mundane tasks, helping humans focus on complex tasks. Although there are concerns about AI’s impact on jobs and privacy, we cannot overlook its benefits, such as improved healthcare, personalized experiences, and enhanced efficiency. AI promises to augment human capabilities, leading to new levels of collaboration and problem-solving.




