The Role of Prototyping in UI/UX Design: Benefits and Approaches
UX Prototyping is a counterfeit of the final product. A shell-like representation of a product that is yet to be finalized. It helps you guide the content and themes of the pages.
Prototyping allows stakeholders and designers to discuss the product’s user flow. The prototype looks as good as the final product. Prototypes can be made up of anything such as paper, sketches, cardboard, white board or anything that can be used to demonstrate the working product that will be developed later.
There is also another type of prototyping that is made up through a series of situations and that is called storyboarding. That is almost like a cartoon with a series of scenes which depicts the user journey of a product. And all the possible scenarios are brought up from the user’s perspective.
Human beings are made in a way that they have a very high visual sense. The human brain contains 30% of the cerebral cortex dedicated to vision. Which makes sense for creating a prototype. And the main thing about a prototype is that you can visualize it!
Prototyping does not only include visual design but also has a complete user experience for users by making it pretend as if that is the final product UI and interactions. It helps everyone involved in the project: UI/UX designers, developers, testers, and users. It helps divulge significant errors and mistakes early to avoid extra work in later stages of product creation.
Reasons why UX Prototyping is Important?
UX prototyping is essential in the UI/UX design of a new product for 2 reasons. I.e., Visualization – helps UX designers showcase how the actual product would look like.
Feedback – it helps generate new ideas and knock out possible errors from the product. It also helps engage potential users and receive experiential feedback on the prototyping and user flow. Prototypes let you inspect various aspects of design and functionalities. And finding errors in the early stage can save a lot of time when creating final product mockups.
But how does the UX prototyping step actually help in improving UX? Or how is it important? Simple.
It leads the UX design process to a further stage by recognizing areas that can be improved in the product.
Prototyping can be done in many ways. Sketches, storyboarding, cardboard models, etc., are examples of prototyping. This also eventually helps stakeholders to think it through and understand the user problems in depth and try to provide a solution to the raised problem. It is also a support to plunge into design research which would otherwise make it easier to get through the errors before developing the product.
Benefits of UX Prototyping
The UX prototyping occurs after creating low-fidelity wireframes and before delivering the final product. There are many benefits of performing UX prototyping, such as:
Evaluation of Research Finding:
The data collected during the initial UX research does not elaborate on the issues arising after delivering the final product. Many errors come to light once the usability testing is done. Performing prototyping and then testing that prototyping helps uncover deep insights and evaluate from initial UX research.
Implementations:
Prototyping supports testing those different ideas and concepts in various forms which is implementable for various stages of the design and iteration process.
Bugs Identification:
Issues in the product are pinpointed, and errors and biases may have yet to come to light during early research.
End-User Confrontation:
Getting users to confront the product in early prototyping helps gather better feedback on product artifacts. It also provides a better understanding and insights that can be useful in developing the proposed product solution.
Saves Stakeholders’ Budget:
Receiving user feedback can make a massive impact in improving the user experiences of the product at no cost, unlike making transitions to already delivered products.
Workflow Simplification:
Once the user flow is decided and all the possible errors are discussed while creating prototypes, the workflow is fixed and maintained without interfering in the workflow and avoiding the extra work for developers to make calculations for UI elements adjustments on the screen. The developer can act according to the plan.
Increase Conversion:
Creating a product does not mean that it is only about product design and development. But instead, it is also about creating a product with a business strategy for backup. The appropriate positioning of the CTAs and navigation points, banners for promotions, and other things can increase stakeholder conversion rates.
Evaluation of Research Finding:
The data collected during the initial UX research by the UI/UX designer does not elaborate on the issues arising after delivering the final product. Many errors come to light once the usability testing is done. Performing prototyping and then testing that prototyping help uncover deep insights and evaluate from initial UX research
UX Prototyping Methods
The prototype is a tactile depiction of your ideas. It can be done in many ways, but generally we all have a similar way of testing and working out the errors before developing the product.
There are a lot of types of prototyping methods. But let’s talk about the major 4 types of prototypes:
Paper Prototypes
The most basic type of prototype is done on paper. You just draw up a screen’s UI on paper and sketch your functionality to showcase how your ideas would work on a digital device.
The paper prototypes are very much less costly as you just have to sketch your ideas on the paper, and then you can brainstorm with your team and stakeholders.
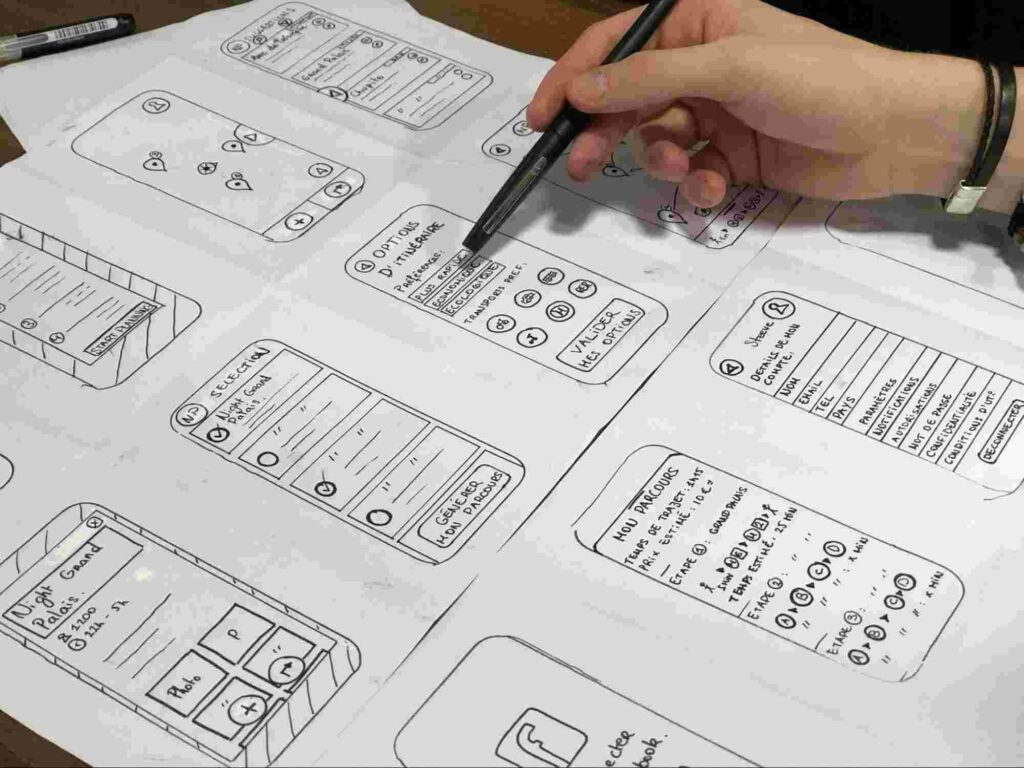
Storyboard Prototyping
This prototyping method is generally used as a driver to focus on the product’s user experience. It is used to design a series of screens that demonstrates how the user would interact with the product from start to end.

HTML Prototyping
This type of prototyping is a basic and early version of the product that works exactly like the imagined final product. But this helps discover possible errors after the final product is delivered.
Digital Prototyping
Digital prototyping is another name for high-fidelity prototypes. It is made to work like real products but with the help of other prototyping softwares that are available in the market. This method is prevalent because it gives a natural product-like feel. And also avails a facility to test all the primary user interface elements.

Tips on Creating Prototype
There is a lot of dependency on the quality of the created prototype. A lot of quality-related things come under observation while creating prototypes. All this depicts the ease of user interface elements, conversion rates, and the user experience of the overall product.
Here are some tips for creating great prototypes:
- Take judgments from other specialists. While providing UI/UX design services with prototyping, many other specialists are involved in the process, such as a copywriter, a marketer, an SEO specialist, and other participants who can help in creating a better product. Consider their judgments and apply those to your design artifacts, adding to your product quality.
- Target audience is everything: Your target audience plays a significant role in your product designing journey. Instead of making assumptions in your design, collect information from your audience. They will give you the perfect answers to all your assumptions. The decreased sales can tell that users need to notice functional UI elements, etc. And then you can work on increasing your target audience.
- Test your product’s functionality: You should always test your prototypes when you sign off the product design for development. Testing your prototype ensures that there are no bugs or errors in the product and your product can run smoothly after it is deployed in the market.
Conclusion
Hence, prototyping is an essential step of the design process. It gives much more clarity on the product design and functionality, saving stakeholders hundreds of bucks and time.
From this, prototyping is an innovative and practical design step that allows you to acknowledge the users’ perspective on the product which is cheap and less expensive in many ways.
“When you’re prototyping you ideas should change constantly” which is why it will be possible to design a even better product.




