Wearable Integration in Custom Healthcare AI Agents

As I was browsing through some studies, I came across an interesting article by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. It stated that one in three Americans uses wearable devices like a smartwatch or a Fitbit to track their health on a regular basis. Interestingly, 80% of these people are willing to share these data points with their care facility or provider.
This is a golden opportunity for healthcare providers to better understand a patient’s health and provide personalized treatment based on the continuous update of health data. And many organizations are making use of wearable healthcare technology to monitor the patient continuously.
However, as I looked into this more, I found a challenge that most healthcare providers face, and that was the conversion of this patient data into actionable insights. The problem here was diverse data formats and, most importantly, data overload. With continuous data flow, it becomes difficult for providers to analyze all the data and bring out useful data.
And as I focused on finding a way to solve this, AI came as the solution, particularly AI agents. With AI agents performing tasks like analyzing and monitoring, they can work as an assistant in managing and analyzing data from wearable devices.
Moreover, if you customize healthcare AI agents using AI wearable medical data integration and vital stream AI, you can easily bridge the gap between wearable devices and meaningful healthcare interventions. You can assign them the task of monitoring, analyzing, and interpreting patients’ vital signs in real-time.
This is why, in this blog, we will explore in detail how custom healthcare AI agents can give you a continuous data source on patient health.
The Wearable Healthcare Landscape: Devices, Data, and Opportunities
The healthcare wearable devices market is thriving, and the variety of healthcare wearable devices is increasing day by day. They came in different shapes and medical data formats, which makes it difficult to keep up with. We have got everything from Apple Watch to FDA-approved continuous glucose monitors.
However, with this variety comes fragmented data formats, varying levels of clinical accuracy, and integration challenges for providers like you. So, I have given a simple breakdown of the ecosystem of popular wearable devices:
| Device Type | Examples | Data Types | Standards/API | Use Cases | Clinical Grade |
| Consumer Wearables | Apple Watch, Fitbit, Samsung, Garmin | HR, SpO2, activity, sleep | Apple HealthKit, Google Fit | Fitness, wellness tracking | No |
| Medical Wearables | Dexcom CGM, Zio Patch, BioIntelliSense | Glucose, ECG, respiratory, temperature | HL7, FHIR, proprietary APIs | Diabetes, cardiac care, RPM | Yes |
| Hybrid Platforms | Withings, Oura Ring | Sleep, temp, HRV, oxygen saturation | Proprietary + FHIR-compatible | Preventive care, chronic care | Partially |
What makes this even more fascinating is how AI can act as the translator between these devices and your clinical systems and bring wearable sync to EHR systems. With the help of custom healthcare AI agents, this can become more efficient and effective, easily converting fragmented data streams into clinically actionable insights.
Seamless EHR & AI Agent Synchronization: Technical Integration Strategies
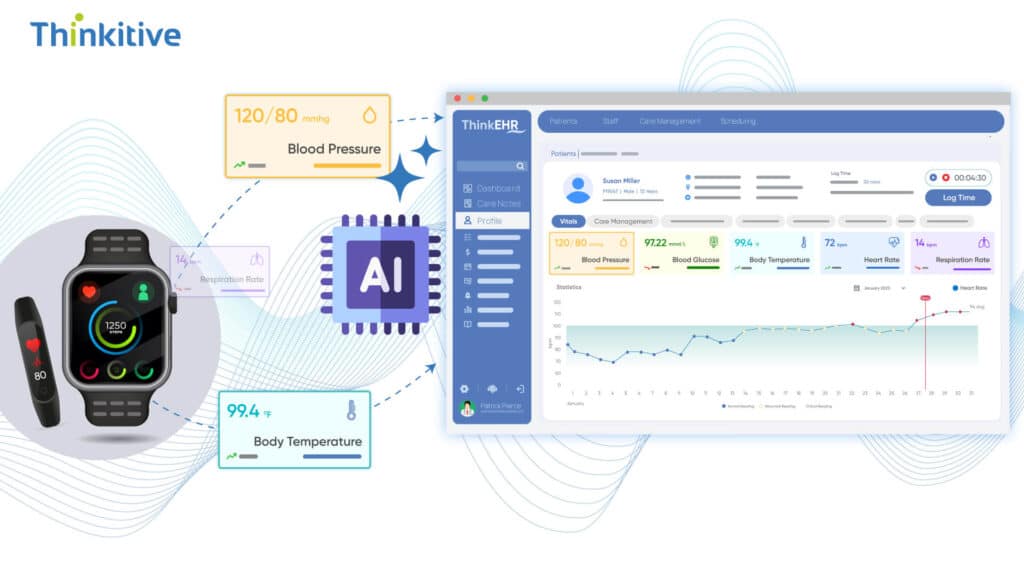
Collecting wearable healthcare data is just the beginning, as you need to convert this data into actionable insights. However, this process of conversion is not simple and faces a challenge, which is the different languages of wearable devices and the EHR systems.
For instance, wearables like FitBit and Apple Watch speak different languages, whereas EHRs like Epic and Cerner need structured and standardized data. That’s where intelligent synchronization strategies come into play.
However, custom healthcare AI agents and AI-powered integration bridge this gap by using APIs and real-time streamlining protocols to ingest, clean, and structure wearable data. With platforms like Apple HealthKit, Google Fit, and the Fitbit Web API, developers can get direct access to patients’ vitals like heart rate and sleep cycles. But the catch is that this data needs to be transformed into healthcare-standard formats like HL7 and FHIR to be used in EHRs.
However, with modern EHR platforms like Epic MyChart and Cerner HealthLife now being able to receive patient-generated data, this problem is almost solved. This is done through middleware and a cloud-based integration engine, allowing custom healthcare AI agents to seamlessly form wearable sync to EHR systems.
Finally, real-time data streaming enables continuous monitoring, alerting, and decision support. With AI agents validating, deduplicating, and routing meaningful data to the right clinical endpoint, decision-making is precise and quick.
Technical Implementation Guide on Wearable-EHR Integration
Free DownloadSignal vs Noise: AI-Powered Data Intelligence & Filtering
When it comes to wearable devices, understanding the collected data is harder than collecting it. With continuous data streams from smartwatches, ECG patches, and fitness trackers, clinicians are not able to sift through multiple interfaces. This is where custom healthcare AI agents step in, not just filters but as intelligent digital team members.
These agents are trained in multiple healthcare environments, patient profiles, and device behavior. With this, detecting and identifying false, low-risk, or data due to device errors becomes possible, allowing only true and high-confidence data to pass.
Additionally, the agents are equipped with context-aware filtering to interpret data in relation to the patient’s lifestyle and clinical conditions. If a heart rate increase is due to exercise or medicine, then it filters it out; however, if it’s unexpected, then it gets flagged.
But things do not end at this; custom healthcare AI agents bring anomaly detection to the table. Unlike one-size-fits-all thresholds, these agents learn from each individual. So, a custom AI agent knows that a slight rise in resting heart rate might be completely normal for one patient, but not for another.
Last but not least, it can correlate wearable data with the patient’s clinical history, creating a multi-dimensional view of patient health. This makes it easier to better understand the patient’s health and changes in the vitals, bringing speed and accuracy.
AI Workflow Integration: From Data to Clinical Action
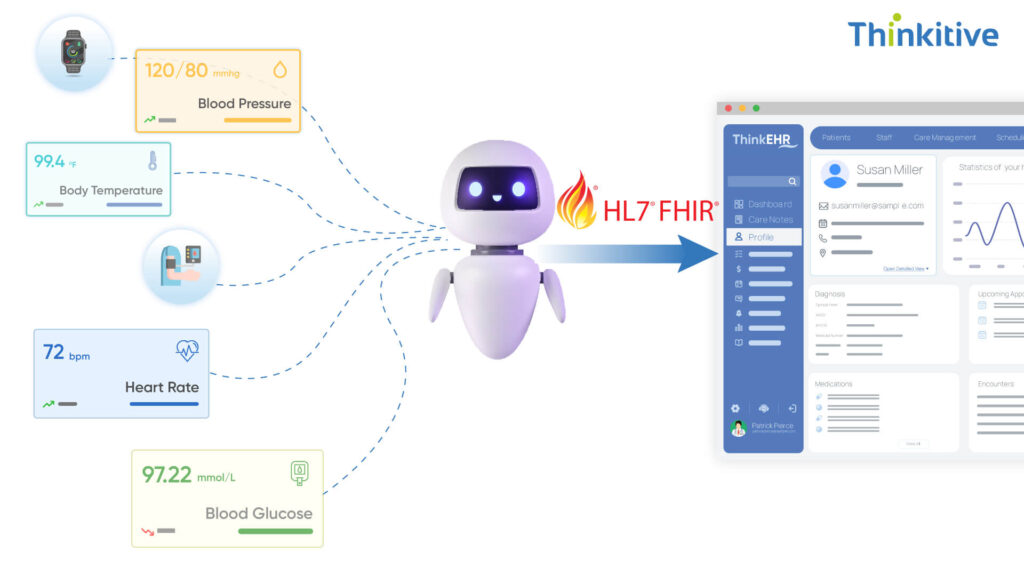
After the collection of data, the next step is crucial as the collected data needs to be converted into real-time clinical actions. Here, custom healthcare AI agents show their true value as they don’t just observe; they actively drive decision-making, care coordination, and early intervention. Here’s how they do it:
1. Risk-Stratified Triage & Alerts: Prioritizing patients based on clinical risk is important to give the needed treatment on time, and data-triage AI makes this process faster. AI agents analyze patient history and real-time wearable data, enabling automated triage and custom AI alerts from devices and setting thresholds so that providers are alerted when a patient truly requires attention.
2. Multi-Parameter Correlation & Pattern Recognition: Rather than focusing on isolated metrics like heart rate or steps, AI agents connect multiple data streams, for example, SpO2 + sleep + glucose, to detect early signs of deterioration or emerging complications with predictive wearable analytics.
3. Contextual Alert Personalization: These AI agents connect with EHR data, medication schedules, and even care plans to ensure that wearable clinical alerts are relevant and timely. This also helps reduce alert fatigue and avoid false positives.
4. Condition-Specific Monitoring Workflows: With custom healthcare AI agents, you can build chronic care monitoring loops for each condition, from diabetes to heart failure. Automate tasks like threshold monitoring, patient outreach, and remote updates by syncing RPM with wearables to care teams based on wearables and historical data.
5. Adaptive Learning & Continuous Optimization: The agent learns from every decision, every ignored alert, and every outcome, creating a continuous improvement loop. It also learns from provider behavior and patient results, refining future alerts and optimizing workflows over time.
Get 20 Wearable Integration Use Cases with Our AI Workflow Templates Library
Download NowSecurity & Compliance: Protecting Patient Data in the Wearable Era
As wearable devices are becoming a core part of patient monitoring, data security and compliance are becoming essential components. No matter what device you are integrating into your clinical system, whether it is a fitness tracker or an FDA-approved medical patch, you need robust security.
Here’s a quick guide to major compliance areas that custom healthcare AI agents and systems must align with when dealing with wearable data:
| Requirement Area | Key Considerations |
| HIPAA Compliance | Enforce PHI access control, encrypted transmission, audit trails, and breach reporting |
| Device Security | End-to-end encryption, secure APIs, and token-based authentication |
| Data Governance | Clear retention policies, patient data ownership, and consent management |
| FDA Regulations | Device validation, intended use compliance, labeling, and reporting standards |
| State Privacy Laws | CCPA, CPRA, and other local regulations on consumer health data |
AI agents that are going to interact with wearable devices must be designed to operate within these strict frameworks. Patient consent is as important as this, especially when you are integrating a consumer device into clinical care. Healthcare systems must be transparent about what data is collected, how it’s used, and who has access to it.
In short, to keep healthcare data from wearable devices safe and maintain its privacy, your AI agents and systems must follow strict regulations and implement robust security measures.
Conclusion
Nowadays, wearable devices are becoming increasingly popular for tracking health parameters like heart rates, sleep cycles, and blood oxygen levels. That’s why leveraging them for remote monitoring can bring benefits for patients and providers both.
With AI-powered wearable integration, along with AI agents developed to handle monitoring, cleaning, and interpreting data, it becomes possible. As healthcare continues to evolve, the combination of AI and wearables will be the key to delivering proactive and personalized patient care.
So, ready to leverage AI-powered wearable integration to make care better by converting passive data into active insights? Click here to transform your care.
Frequently Asked Questions
AI agents integrate with wearables like Apple Watch and Fitbit through APIs and SDKs, enabling real-time access to health metrics such as heart rate, activity, and sleep data. This allows Fitbit/Apple Health AI to analyze trends, deliver personalized insights, trigger alerts, and support proactive care and chronic condition management.
Consumer wearables can extract valuable medical data like heart rate, blood oxygen (SpO2), ECG readings, sleep patterns, physical activity levels, body temperature, and stress indicators. When integrated with clinical systems, this data supports chronic care management, early disease detection, remote monitoring, and personalized treatment planning.
AI filters meaningful health signals from wearable device noise by using advanced signal processing, machine learning, and contextual algorithms. It distinguishes real physiological patterns from artifacts by analyzing trends, comparing them with baseline data, and filtering out motion-induced or environmental distortions for accurate, actionable insights.
Yes, wearable data can be automatically synchronized with EHR systems like Epic or Cerner using APIs, HL7/FHIR standards, and integration platforms. This allows real-time transfer of patient vitals and activity data, enhancing remote monitoring, chronic care management, and clinical decision-making within provider workflows.
HIPAA compliance for wearable healthcare AI integration requires secure data transmission, encryption, and access controls. Covered entities must ensure patient consent, implement audit trails, and partner only with HIPAA-compliant vendors. The AI system must safeguard protected health information (PHI) throughout data collection, processing, and sharing.
AI alerts from wearable devices reduce false positives and alarm fatigue by analyzing continuous data patterns, filtering out noise, and prioritizing alerts based on clinical relevance. They learn patient-specific baselines, ensuring only actionable, context-aware notifications are sent to providers, improving response time while avoiding unnecessary disruptions.
Medical-grade wearables offer higher accuracy, typically validated through clinical trials and FDA clearance. In contrast, consumer wearables prioritize convenience and general wellness, leading to wider variability in data, especially for metrics like heart rate or oxygen levels. The accuracy gap is significant in clinical decision-making contexts.
Healthcare providers can use wearable AI devices to track real-time patient vitals like heart rate, glucose levels, and oxygen saturation remotely. These devices enable proactive interventions by detecting anomalies early, enhancing chronic care management, reducing hospital readmissions, and ensuring continuous, personalized monitoring outside clinical settings.
Security measures include end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure APIs to protect data transmission. HIPAA compliance ensures privacy standards, while AI algorithms monitor for anomalies and threats. Additionally, regular firmware updates and access controls prevent unauthorized access to patient data collected via wearables.
Implementing wearable AI integration in healthcare typically takes 3 to 9 months, depending on the scope, data infrastructure, and regulatory requirements. Timelines can extend if custom APIs, EHR integration, or HIPAA-compliant security layers are involved. Pilot testing and staff training also influence rollout speed.




