What is Remote Patient Monitoring?
A remote patient monitoring service is revolutionizing the delivery of preventative healthcare in the US. Providers can reap significant benefits by adopting remote patient monitoring (RPM) and implementing RPM programs. Consequently, they will be able to offer better treatment to patients and increase their revenue.
Moreover, remote patient monitoring is a cutting-edge healthcare platform that leverages modern technologies. It effectively caters to patients who are situated far from clinics or hospitals. The platform incorporates technical tools, medical sensors, devieces, and platforms to ensure high-quality care for these individuals.

However, Providers can use these tools to transmit and access patient health records electronically. This ensures compliance with HIPAA security standards and patient health data security.
RPM typically involves wearable sensors and devices. Examples include blood pressure monitors, glucometers, and activity trackers. These devices are connected to a patient’s smartphone or tablet.
Offering Remote patient monitoring services can make your organization more marketable. This may also increase providers’ recurring revenue.
This offering lets your provider closely monitor your patients without visiting a doctor’s office. This can lead to more control over patients’ chronic conditions and overall health.
Medicare started paying for RPM services. CMS began paying monthly providers for time, capable devices, and initial setup and education costs. They also require clinicians to offer remote services to their patients.
To do so, physicians must have relevant patient records with their history. This is necessary to provide RPM services.
Who Qualifies for RPM?
People suffering from at least one chronic condition for six months must be monitored regularly to prevent further harm.
Some of the Examples of chronic conditions that can be managed in RPM but aren’t limited to:
1. Asthma
2. Cancer
3. Cardiovascular disease
4. Depression
5. Diabetes
6. Hypertension
7. Infectious diseases like HIV and AIDS CPT
Who can Perform RPM?
Physicians and Non-Physician Practitioners can provide RPM services and be billed for the same. Below are some examples of RPM service providers other than Physicians.
1. Certified Nurse Midwives
2. Clinical Nurse Specialists
3. Nurse Practitioners
4. Physician Assistants
How Does Remote Patient Monitoring Work

Remote patient monitoring (RPM) involves using technology to monitor patients’ health outside a traditional clinical setting, such as in their homes. Here’s how it typically works:
Enroll Patients in RPM Services
First, Providers need to enroll the patient into RPM service, for this provider and patient can meet virtually or in person. Provider collects all patient demographics and clinical details. As the patient qualifies for CMS eligibility checks for RPM services, the provider can enroll them in RPM services.
Initial Setup and Patient Education
After enrollment, the provider creates a care program for the patient based on their chronic disease. This care program includes the patient’s chronic conditions and goals which must be achieved to recover from them. Providers must track the patient’s vitals and activity to achieve these goals.
The provider educates the patient when assigning care programs and devices. They teach the patient how to use the device and comply with the care program for better health outcomes.
Patient Vital Collection and Transmission
Wireless technology, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, facilitates the collection of patients’ vital signs and health data by healthcare providers. Wearable devices, sensors, or mobile apps are vital in gathering real-time information, including blood pressure, heart rate, blood glucose levels, and oxygen saturation.
The collected data is transmitted directly to healthcare providers or monitoring centers through wireless cloud services. This remote monitoring capability allows providers to detect potential abnormalities early, ensuring prompt intervention.
Provider Review and Analysis of Data
The data will be available on the provider’s desk to review. They will review it and make comments as necessary.
Researchers or analysts can analyze this data to identify patterns or trends. Moreover, they can utilize specialized software or algorithms to perform this analysis. Consequently, these patterns or trends may indicate a deterioration in the patient’s health. If abnormalities are detected, providers can take action. This action, in turn, may include adjusting medication or scheduling a virtual visit with the patient.
Communication with Patients
Remote patient monitoring also involves regular communication between healthcare providers and patients through virtual visits or messaging apps. This allows healthcare providers to assess the patient’s overall health status and provide guidance on managing their condition.
This communication ensures all security standards that secure patient and provider communication by following HIPAA-compliant guidelines.
Benefits of Remote Patient Monitoring
The benefits of RPM are numerous.
First and foremost, it enables healthcare providers to closely monitor patients’ health conditions and identify potential risks before they become serious. This can lead to early interventions and improved outcomes.
Technology tools and medical devices can monitor patients away from healthcare facilities. This is a distinct advantage, allowing them to remain at home.
Below are some of the critical benefits of RPM:
1. Automated patient data collection and transmissions.
2. Medical devices make it easier to collect patient vitals.
3. Better patient engagment using technology for two-way Messaging and Tele-calling.
4. CMS pays for RPM, Its cost-effective service for patients.
5. By continuous monitoring, Providers can identify future risks of any chronic illnesses and be able to take preventive actions. This may lead to saving hospitalization expenses.
6. Optimizing staff burning rate
7. Reduces clinic visits resulting in minimizing the spread of infectious diseases.
The Revenue Model for RPM
The Centre of Medicaid and Medicare Services (CMS) established the CPT codes for remote patient monitoring services based on the time spent by the provider for each patient. Consequently, RPM service providers can now submit a claim for reimbursement using these qualified CPT codes.
Payers carefully validate the monthly RPM report, time log, patient outcome, and tracking history to facilitate payment. Subsequently, they make payments to the provider accordingly.
Below are the CPT codes used in RPM to bill:
99453 : Initial Setup and Education
99454 : Monthly 16 days Check Compliance
99457 : Monthly initial 20 mins monitoring
99458 : Consequent Additional 20 mins monitoring
Devices Used for Remote Patient Monitoring
Currently, in the market, a variety of RPM devices are available. Below are the most commonly used devices. Let’s have a quick look at them:
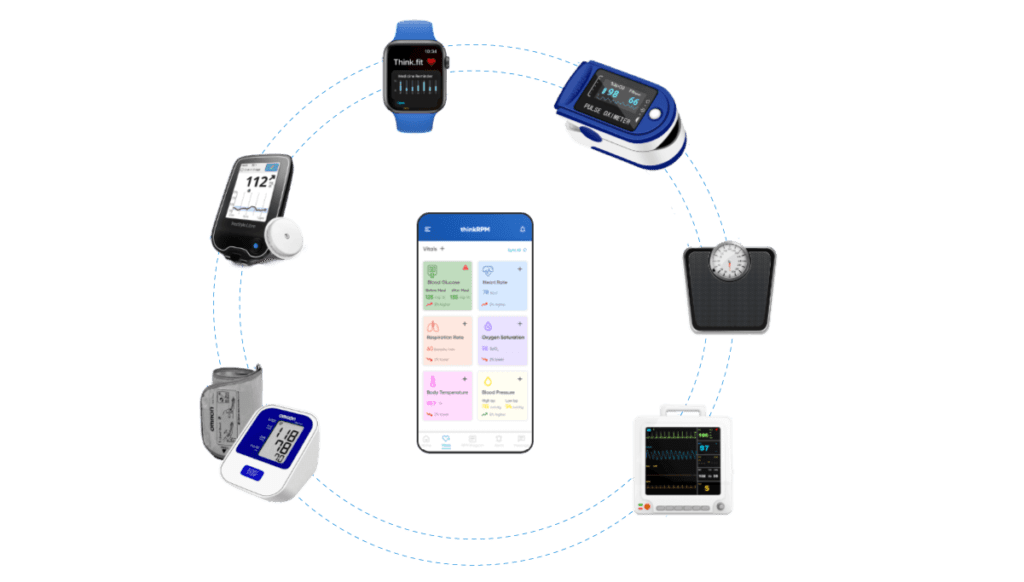
- Blood Pressure Monitoring Device
This device enables healthcare providers to track patients’ blood pressure readings from a distance. This is very important for chronic illnesses like hypertension or heart disease.
- Weight Monitor
A weight monitor is essential for remote patient monitoring (RPM). RPM allows healthcare providers to follow changes in a patient’s weight. This helps them to track progress over time. Patients with chronic conditions such as heart failure or kidney disease use it.
- Blood Glucose Monitor
Remote patient monitoring utilizes a blood glucose monitor to track patients’ blood sugar levels with diabetes or other conditions. Consequently, this allows medical professionals to provide timely interventions or adjustments to the treatment plan if necessary.
- Pulse Oximeter
Remote patient monitoring can use a pulse oximeter to measure oxygen levels. This is done even when patients are not physically in a healthcare setting.
Patients can wear a pulse oximeter on their fingers, earlobe, or toe. This device measures oxygen saturation level and pulse rate.
Pulse oximeters are particularly useful in monitoring patients with respiratory conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or COVID-19.
- ECG
Remote patient monitoring utilizes Electrocardiogram (ECG) to track heart health, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients outside medical facilities. Moreover, wearable devices can record and transmit real-time ECG data to healthcare providers. As a result, remote ECG monitoring can detect and diagnose various heart conditions.
- Wearable Devices
Electronic devices worn on the body, typically on the wrist, chest, or ankle, are known as wearables. In remote patient monitoring, healthcare providers often utilize wearable devices to monitor various health parameters of patients in real time.
Wearable devices can collect various data types, such as heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, oxygen saturation, and physical activity levels. They transmit this data wirelessly to healthcare providers for analysis, enabling them to monitor a patient’s health remotely.
Difference Between Remote Patient Monitoring & Remote Therapeutic Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring is a digital method of monitoring patient health. It captures objective health data using technology provided by physicians, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners. Similarly, remote therapeutic monitoring is another technology used in healthcare services. Provided by physical therapists, occupational therapists, and speech-language pathologists, this technology is specifically employed to manage orthopedic and non-physiological conditions.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote patient monitoring enables providers to track patients’ physiological health data using technology and medical devices at home. These devices include BP monitors, blood glucose monitors, wearables, and pulse oximeters. All collect patient vitals and transmit them electronically to the caregiver.
Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM)
Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM) is a healthcare practice. It utilizes technology to collect non-physiological and musculoskeletal information from patients. This allows for personalized therapeutic interventions.
RTM also provides interactive feedback and support. It enables healthcare providers to make evidence-based decisions about treatments and interventions for individual patients.
Key Differences between RPM and RTM
RPM focuses on monitoring a patient’s health, while RTM focuses on monitoring the effectiveness of a patient’s treatment. Both technologies use similar methods to collect data but use it for different purposes.
RTM is similar to RPM. However, it differs in that RTM involves patient management using medical devices. These devices collect patient therapeutic data, such as adherence to therapy, treatment response, respiratory system conditions and progress, and musculoskeletal system.
RPM and RTM can be billed separately for different services for different CPT codes assigned by CMS.
Thinkitive’s Remote Patient Monitoring Solutions
Thinkitive designs remote patient monitoring solutions, facilitating real-time tracking of patients’ health conditions, regardless of location. These solutions utilize connected devices and mobile applications to gather and send patient data to healthcare providers and caregivers, including vital signs, medication adherence, and symptom tracking.
By implementing Thinkitive’s remote patient monitoring solutions, healthcare providers can enhance their ability to manage chronic conditions while reducing hospital readmissions and improving patient outcomes. This is achieved by enabling proactive and personalized care, granting patients greater flexibility and convenience. RPM, short for Remote Patient Monitoring, empowers patients to receive medical care without the need to visit a physical location.
Some of the features of Thinkitive’s Remote Patient Monitoring Solutions include:
1. Connected devices such as blood pressure monitors, glucose meters, and weight scales
2. Mobile applications for patient data collection and symptom tracking
3. Cloud-based platforms for data storage and analysis
4. Real-time alerts and notifications for healthcare providers and patients
5. Secure messaging and communication tools for care coordination
Conclusion
Thinkitive’s remote patient monitoring solutions can improve healthcare providers’ ability to manage chronic conditions. They can also help to prevent hospital readmissions and improve patient outcomes. This is achieved by enabling proactive and personalized care. Solutions can give patients more flexibility and convenience. This allows them to get care in the comfort of their own home.




