What is Human Centered Design and Why is it Important

Human-centered design is an emerging norm in the product development world. It aids businesses in developing products that clients adore and are willing to pay for. It is believed that the concept of human-centered design and engineering began in 1958 at Stanford University during the design program when Professor John E. Arnold proposed that engineering design should be centered on people and aimed at creating positive and long-lasting change.
The idea has since been applied to a wide range of disciplines outside of engineering, such as psychology and anthropology, and it continues to offer an innovative approach to problem-solving that will support the advancement of innovation in a way anchored in user happiness and human well-being.
What precisely is human-centered design, and how does it contribute to meeting the actual needs of individuals and committees? Here is all you need to know about this idea, from how it works to how human-centered design thinking frequently generates more creative ideas and practical solutions than the newest, hottest technological developments.
What is human-centered design (HCD)?
Human-centered designs are the idea of developing and innovating goods and services in response to issues or gaps that will advance human welfare, enhance user experience, and lessen human suffering or stress. The process does not rely on technology or artificial intelligence to advance a concept or product; instead, it involves human brainstorming and context at every stage of the problem-solving process.
The participatory action research idea of using actual human behavior and responses to find flaws in projects or offer the chance to improve upon current goods or services to enhance the overall user experience or offer creative answers to issues in a given community or group of people is extended by the idea of human-centered design.
Although this idea is most frequently applied to enhance or solve issues in the health and wellness sector, it is quickly gaining popularity as an approach for evaluating and improving the technologies we use daily. The most prevalent instance of human-centered design and engineering in technology was the participatory action research that led to Apple changing the iPhone to include unique features that aid in improving the overall UX; as a result, it was established that Blackberry phones are far lower human usability than iPhones.
4 Principles of Human-Centered Design

A human-centered design approach aims to alter how companies view their goods and services rather than to give specific guidelines for constructing various solutions. Because of this, it’s essential to understand the theoretical support of best practices in addition to putting them into practice. The fundamental principles of the human-centered design process are as follows:
People-Centered
Although the notion of human-centered design makes this principle appear simple, it requires further explanation. When designing a product, the UX design team should think of it as a tool that must address the concerns of actual people to keep the user at the center of the development process. The human perspective must be investigated at every level of the product development process. In addition, to user needs, product UX design companies should consider current limitations, preferences, desires, and the entire context.
Solve the Right Problem.
Human-centered design methodology has two kinds of issues; fundamental and symptomatic. Instead of “curing” the symptoms, the objective is to identify the core issue and offer a workable remedy. You must conduct an in-depth investigation to pinpoint the cause of people’s suffering. At first glance, the root of the issue could be obvious, and you don’t need to spend time looking for it. However, if this happens, you can create a product that addresses an unsolvable or incorrect issue.
Take a Systematic Approach
The actual world connects everything. That’s why resolving a local issue does not solve the original issue in the long run. You must consider the whole user journey while using human-centered design. Put yourself in a buyer’s shoes at each stage of the purchasing process, for instance, if you want to build an online store using HCD methodology. This implies you can’t focus on improving the product search while ignoring the awkward checkout. The focus of the entire solution, as well as each of its components, should be on the people.
Focus On the End Result
One thing you’ll notice about instances of a human-centered approach is that they all emphasize the final product rather than the means to get there. A tool’s user experience (UX) ought to be clear and provide a seamless transition from one touchpoint to another. However, the focus must be on the outcome that a user ultimately achieves with the aid of the tool. For instance, a camera should fulfill users’ desire to take attractive pictures. Even though the device’s specifics are crucial, they are useless if a person cannot use it to acquire the desired effect.
Human-Centered Design Process
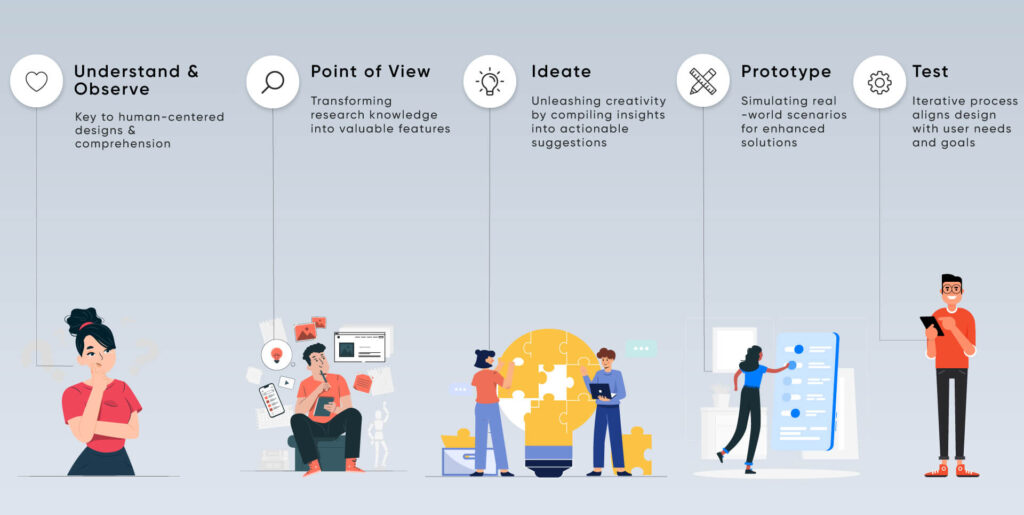
The three overlapping stages of the human-centered design process are inspiration, creativity, and implementation. While gathering inspiration, you will fully engage with the individuals you are creating to understand their needs and desires. You will consider what you have learned throughout the ideation phase, then generate, prototype, and test potential solutions. The final stage of implementation is where change will occur. You will implement your solution at this phase, knowing that the individuals who encountered the issue were an integral part of the design process and even a design team member.
Understand and Observe
Empathy is the first step in creating human-centered designs, which is crucial for comprehension. Empathy, or the capacity to identify with individuals experiencing the problem, is crucial because it allows for a greater understanding of how to develop solutions through what you design and produce. Great research techniques like interviews, immersion, or led tours can aid the process of developing empathy and understanding.
Point of View
After learning about human needs, the next stage is to combine knowledge and establish a viewpoint. Understanding how the knowledge gathered via research transforms into the features of a good or service is called synthesis. You can progress through this process from data to information, knowledge to wisdom, and wisdom to knowledge.
Ideate
Creativity occurs after insights are compiled into needs and suggestions that can be implemented. Idea generation is to produce as many unique concepts as feasible. Even if your ideas are unrealistic, the psychological advantage comes from defeating your inner critic, frequently preventing you from coming up with disruptive or paradigm-shifting answers. According to research, having a wider variety and quantity of thoughts results in the best ideas.
Prototype
Using prototypes enables you to test a design in a setting as close to actual use as feasible. This provides the complete contextual information needed to enhance a solution. Prototyping addresses essential questions about business and product assumptions and is an excellent way to understand someone’s experience in the user context.
Test
Testing validates important presumptions about a product design, service design, or business model. Additionally, it offers a tool to look into potential strategic prospects for increased value creation and income growth. Designers develop quantitative and qualitative usability metrics to comprehend what is effective and ineffective. In human-centered design, the iterative testing process lets you gradually develop a design that closely fits the user’s actions, objectives, and requirements.
Why is Human-Centered Design Important?
Designing with the needs of people in mind is not a fad that has no relevance to anyone’s life. The framework benefits everyone involved in the development process and can significantly enhance how individuals approach various activities.
Let’s examine why effective product development depends so heavily on human-centered design.
1. Advantages for users:
- The foundation of the human-centered design paradigm is the individual and their needs. Users thus receive items that are specifically designed to address their problems.
2. Advantages for stakeholders:
- The more excellent potential parties for solutions developed using the HCD techniques to gain a sizable market share. Additionally, because individuals prefer to feel cared for, they promote client loyalty to a brand.
3. Advantages for developers:
- Programmers’ tasks are made more accessible by human-centered design since they may rely on information verified through user testing and market research. So stop making assumptions now.
Additionally, a team that adheres to a system development life cycle is psychologically more result-oriented. A client can anticipate a higher return on investment because it will waste less work.
Conclusion
Human-centered design thinking prioritizes the problems and requirements of people to produce usable and meaningful digital products. Using human-centered design, businesses can create products that genuinely benefit people and foster empathy with them. You may be confident that your investments won’t be wasted on a product nobody needs if you use the HCD approach in your product development process.
A development team will go in the proper direction and deliver a functional and profitable product with the help of research, testing, and frequent iterations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Human-centered design is an approach to design that puts the needs and experiences of the user at the center of the design process. This means that the designer focuses on understanding the user’s needs, behaviors, and preferences and then designs a product or service that meets those needs. This allows designers to create more effective, efficient, and enjoyable products. Human-centered design is about creating products for people rather than forcing people to adapt to the product.
Human-centered design focuses on understanding the needs and behaviors of the people who will use a product or service. The approach puts the user at the center of the design process. The three key features of human-centered design are:
- Understanding the user’s needs
- Understanding user behaviors
- Understanding User’s Preferences
Designing a product or service that meets those needs and creating products designed for people to adapt to the product. This approach allows designers to create more effective, efficient, and enjoyable products.
Good human-centered design is an approach to design that focuses on understanding the needs and behaviors of the people who will use a product or service. It involves putting the user at the center of the design process and designing a product or service that meets those needs. Designers should make products that are easy to use, intuitive, and accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. By following human-centered design principles, designers can create more effective, efficient, and enjoyable products.
The human-centered design aims to create products and services tailored to the needs, behaviors, and preferences of the people who will use them. By putting the user at the center of the design process and designing products that are intuitive and accessible, designers can create more effective, efficient, and enjoyable products. Human-centered design involves:
- Understanding the user’s needs, behaviors, and preferences.
- Designing a product or service that meets those needs.
- Creating products designed for people rather than forcing people to adapt to the product.




